
Registered Nurses are commonly called RNs. An RN has a four-year baccalaureate degree in nursing from a university or its international equivalent. Nursing is a field that is continually developing.
The best part of nursing as a profession is the capacity to work in many sorts of conditions and a wide range of jobs.
There are two types of jobs for RNs, consisting of hospital-based jobs and non-hospital-based jobs. Hospital-based jobs for RNs include different specialties ranging from Burn Care Nurse to Cardiac Care nurses. Non-hospital-based jobs comprise Clinical Nurse Educator, Travel Nurse, and Nurse Writer.
If you’ve earned your nursing degree, you’re likely excited to get to work. There are a lot of jobs you can work with a nursing degree, but nailing down the right position can be overwhelming.
This article explores different nursing jobs and the types of practices where nurses work.
Types of Jobs for Registered Nurses
1. Hospital-Based Jobs
The RN works in a joint effort with the Bedside Nurse and interdisciplinary team to support the care of patients in hospitals. An RN may work in more management or administrative capacities in a hospital that is briefly discussed below. Let’s have a look to get a complete understanding of registered nurse jobs options.
Ambulatory Care Nurse

Ambulatory care nurses offer high-quality nursing care in an outpatient setting. This nurse can work in a clinic, university health center, medical office, government institution, or other healthcare sectors where patients don’t need to stay overnight.
They perform several tasks, including assessing symptoms, providing care for injury or illness, taking vital signs, and any number of general nursing duties for patients.
Burn Care Nurse
Burn care nurses are those who care for patients who have got physical wounds due to burns. This includes the instant stabilization of acutely burned patients, cleaning and dressing their burn wounds, and relieving the pain and rehabilitation. Burn care nurses often work in the ICU or Burn Care Units (BCUs) of hospitals.
They play a significant role in assessing a patient’s emotional and psychological well-being and ensuring patients receive compassionate care as they recover physically and emotionally from their injuries.
Camp Nurse

Camp nurses serve to provide care to campers and staff in residential and day camps. They can work solo or independently. Camp nurses must have excellent clinical and management skills.
They complete pre-camp health assessments and treat everything, including colds, bug bites, and allergies.
RNs with a background in pediatrics, emergency care, or trauma are best suited for this role, as providing care to children with urgent and non-urgent medical needs is a large part of the job.
Cardiac Care Nurse
Cardiac care nurses are responsible for treating patients with heart diseases or problems. They can provide cardiac and vascular monitoring, perform stress-test evaluations, administer medication, and help with pain management in cardiac patients.
They also tend to post-op patients who are on the way to recovery from bypasses, pacemaker implants, or other heart surgeries. Cardiac care nurses work in cardiovascular centers, hospitals, and other healthcare environments and work with patients of all ages.
Nurse Case Manager
Nurse case managers are those who work with patients and their medical teams to develop, coordinate and implement comprehensive medical care plans throughout an illness.
This is an especially rewarding field of nursing that allows RNs to develop long-term relationships with their patients, educate patients and their caregivers on their treatment options.
Case management nurses coordinate doctors’ appointments and surgeries and have the opportunities to work in a variety of healthcare sectors, ranging from clinics and hospitals to hospice facilities and nursing homes.
Charge Nurse

The charge nurse supervises the staff nurses in hospital wards and other busy medical facilities. They provide staff guidance, maintain supplies, set schedules, and oversee patient care and education. Charge nurses can also treat patients themselves and sometimes take control when a medical emergency is faced.
A mix of clinical as well as supervisory leadership skills are required to excel in this role.
Chief Nursing Officer

Chief Nursing Officer (CNOs) is a high-level nursing executive who serves as administrative leaders within healthcare sectors. They coordinate and check the activities within the nursing department, along with facilitating operations and the patient care experience.
This management role requires extensive nursing experience and an advanced nursing degree such as an MSN or DNP, often alongside an MHA or MBA degree.
Dermatology Nurse

Dermatology nurse provides care and treatment for patients with various skin problems and diseases such as skin cancer, psoriasis, and acne. In addition to assisting skin examinations, dermatology nurses also perform cosmetic dermatology treatments like chemical peels.
In response to the increased cases of skin cancer in the United States, dermatology nurses focus on early detection, treatment, and patient education on how they can prevent skin cancer.
Director of Nursing
Nursing Directors are also known as Directors of Nursing (DON). They have the responsibilities in an administrative area combing years of clinical nursing experience, managerial skills, and education to develop organizational structure and care standards.
They coordinate and check nursing staff, review the budgets, and manage the nursing department. This high-level nursing position requires extensive education and experience.
Emergency Room Nurse
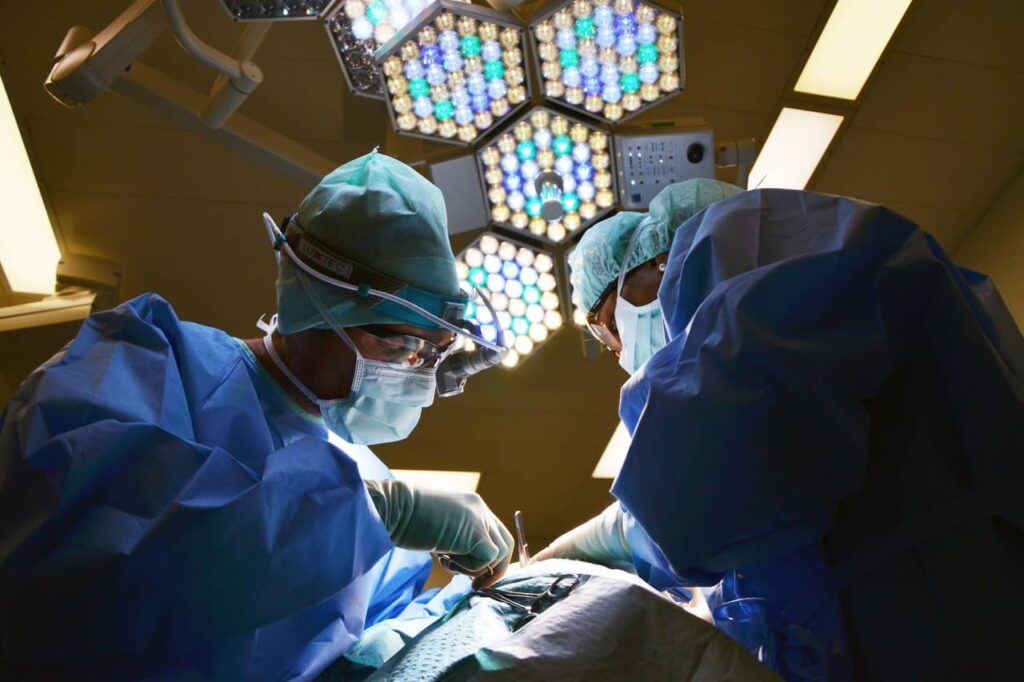
‘Emergency Room’ nurses are extremely efficient, effective, and calm. Their presence and skills are general as the Emergency Rooms admit all kinds of patients with different kinds of trauma. They are highly specialized in assessing, triaging, and caring for sudden accident or illness victims.
With a varied intake, depending on the day and sometimes on the hour, the ER nurses are responsible for continuously prioritizing the needs of the patients in the emergency ward to ensure everyone remains stable as doctors move to admit, treat, or refer to ancillary care.
Fertility Nurse
Fertility or reproductive nurse treats and educates patients and couples on all areas about fertility (i.e., fertility treatments, egg donation and IVF, issues with conception, and more). They can work in reproductive centers to assist physicians with fertility treatments and procedures or focus on counseling and education.
They can also assist researchers with the latest scientific advancements in reproductive technology.
Geriatric Nurse
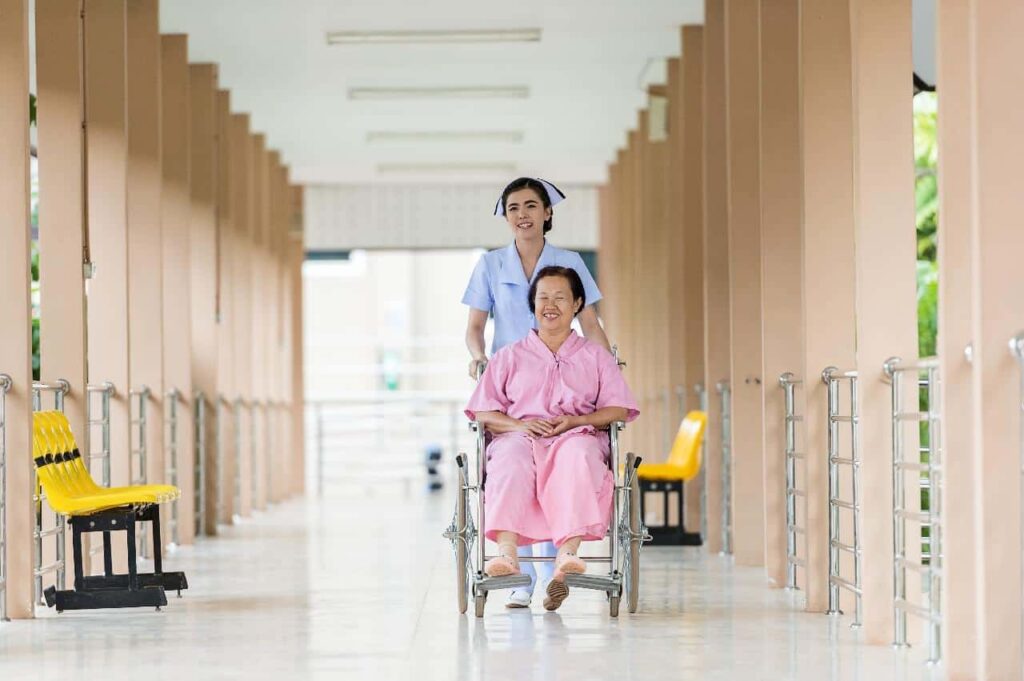

Geriatric nurses deal with elderly patients in various settings, such as hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, nursing homes, home healthcare, and more. They help to maintain functional mobility, medication management, bedside nursing, and more.
Hospice Nurse
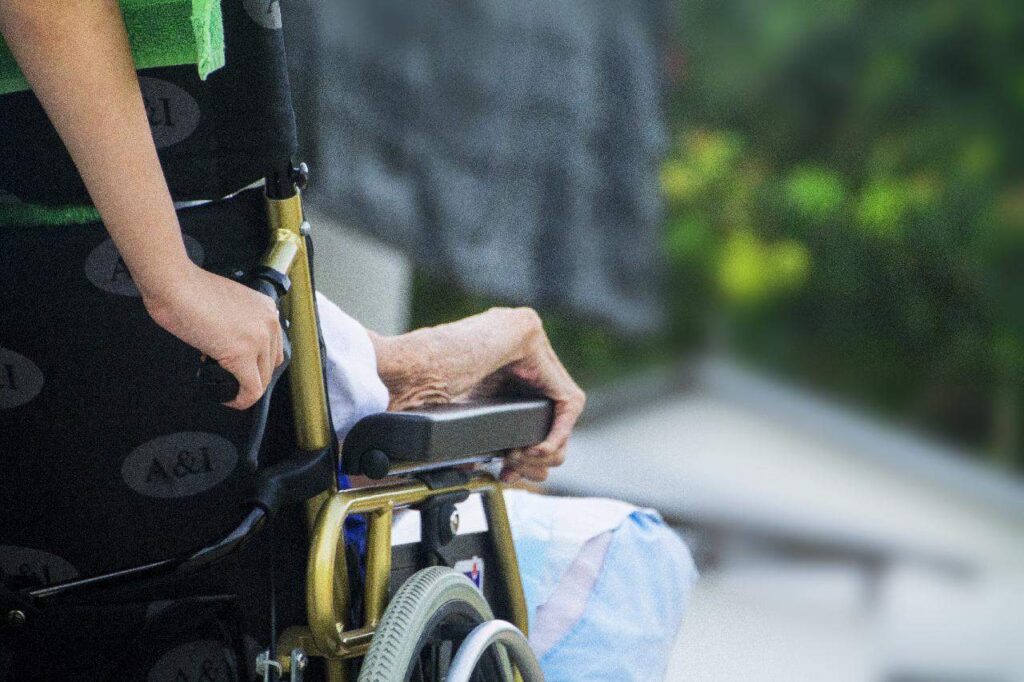

Hospice nurses care for the patients who are at the end of their lives. They make sure to make them as comfortable as possible by managing their symptoms, maintaining hygiene, and administering medications.
Hospice nurses also provide support and communication to the family and other caregivers. They typically work in hospitals, private homes, nursing homes, or hospice centers.
ICU Nurse
Intensive care nurses, also called ‘Critical Care’ nurses or simply ICU nurses, are a specialized and trained subsection of the nursing profession. With a low patient-to-nurse ratio, the ICU nurse is responsible for the individual tasks and subtasks involved in caring for a patient to stabilize their condition.
Sometimes, intensive care nurses work with patients out of surgery, during complicated phases of the disease, post-trauma, and those who are transitioning to end-of-life care measures.
Infection Control Nurse
Infection control nurses are specialized in preventing the spread of infectious agents, like viruses and bacteria. They work hard to prevent and control infectious outbreaks in hospitals and other healthcare sectors.
They develop plans, implement infection control practices, and educate and train staff in order to bring the rate of infections down within a particular facility and prevent outbreaks. They may also act as coordinators and leaders if any outbreaks occur.
Labor and Delivery Nurse

A Labor and Delivery (L&D) RN ensures the safety of both mother and infant during the birth process. They work with the interdisciplinary team in order to bring life safely into the world. The L&D nurses must think and act quickly while constantly dealing with emergencies and initiating appropriate interventions.
This RN assists with cesarean sections, initiates and monitors fetal heart rates, monitors and assists with epidurals, induces labor, and ultimately works to find the safest and most effective ways to have healthy childbirth.
Legal Nurse Consultant
A legal nurse consultant is a highly educated RN who works as an expert on medical issues cases. They can work in law offices, hospitals, government agencies, and insurance companies. Their duties include reviewing and summarizing medical records, serving as expert witnesses, investigating patient claims, auditing medical bills, and more.
Military Nurse

Military nurses are those who serve in a branch of the military and are specially trained to provide medical care to the patients in military clinics or hospitals or the makeshift medical facilities near the combat zones. They care for soldiers or other military personnel, veterans, and service members’ families.
Military nurses need to make at least a three-year commitment to serve their country, but in return, they can receive benefits such as housing stipends, student loan repayment, and pensions.
Nephrology Nurse
Nephrology nurses care for those patients who have or are at risk for, kidney problems including kidney transplants, Chronic Kidney Disease, and other issues. They may perform dialysis, monitor patients, help manage symptoms, provide prevention information and education, and more.
They usually work in hospitals, clinics, dialysis centers, and physicians’ offices.
NICU Nurse

Neonatal Intensive Care Unit nurses are also known as NICU nurses. They care for newborns who have a variety of medical ailments, including premature congenital disabilities, dangerous infections, cardiac malformations, and more.
In addition to treating these newborns, they also train and educate families on how to care for the infants and communicate with them about the infant’s treatment and progress. They mainly work in the NICU department of hospitals, although they can occasionally work in other settings.
Obstetrics (OB) Nurse
Obstetrics (OB) nurses are those who care for female patients before, during, and after the pregnancy and birth of the child. They help an OB/GYN doctor with prenatal checkups, screenings, ultrasounds, and the childbirth process.
In addition, they can also assist with other women’s health issues like birth control information, infertility, and cancer screenings. They mostly work in OB/GYN physician offices, maternity wards in hospitals, or in birthing centers, though they can work in areas such as urgent care as well.
Operating Room Nurse
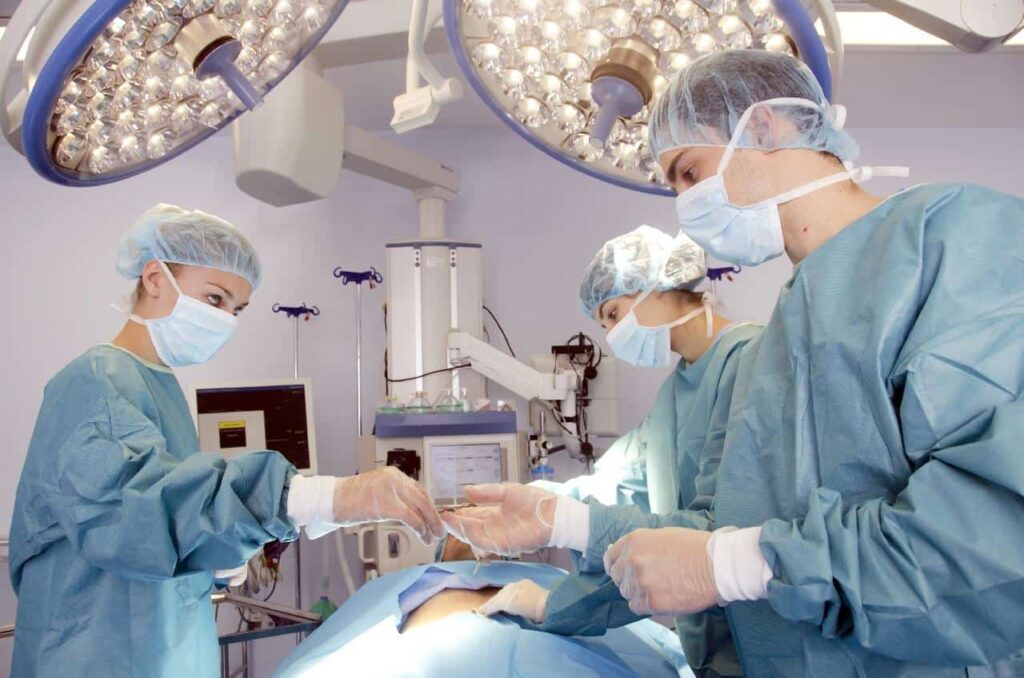
In all aspects of pre-surgery, whether intra-surgery or post-surgery, there’s an OR nurse who helps navigate the process, assisting the surgical team, providing care for the patient, and educating the patient’s family.
An OR nurse promotes the health and welfare of the patient under various conditions. With the promotion of a supportive, positive, and care-focused environment, the OR nurse is a valuable addition to many hospitals, doctor’s offices, and clinics.
Perianesthesia Nurse
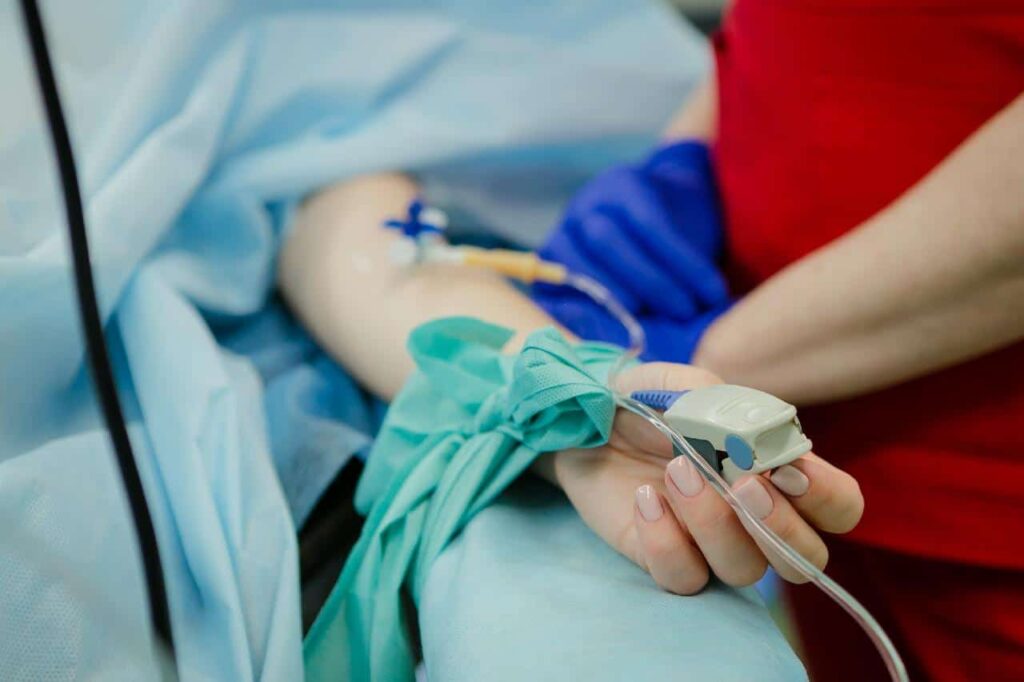
Perianesthesia nurses prepare patients for surgery, but their major duty is to care for patients coming off of anesthesia or sedation after a surgical procedure.
They help orient the patient, checking vitals, including blood pressure and respiration rate, and making sure the patient is not suffering from any side effects or adverse reactions from anesthesia. They most commonly work in hospitals, in Post-Anesthesia Care Units (PACUs).
Perinatal Nurse
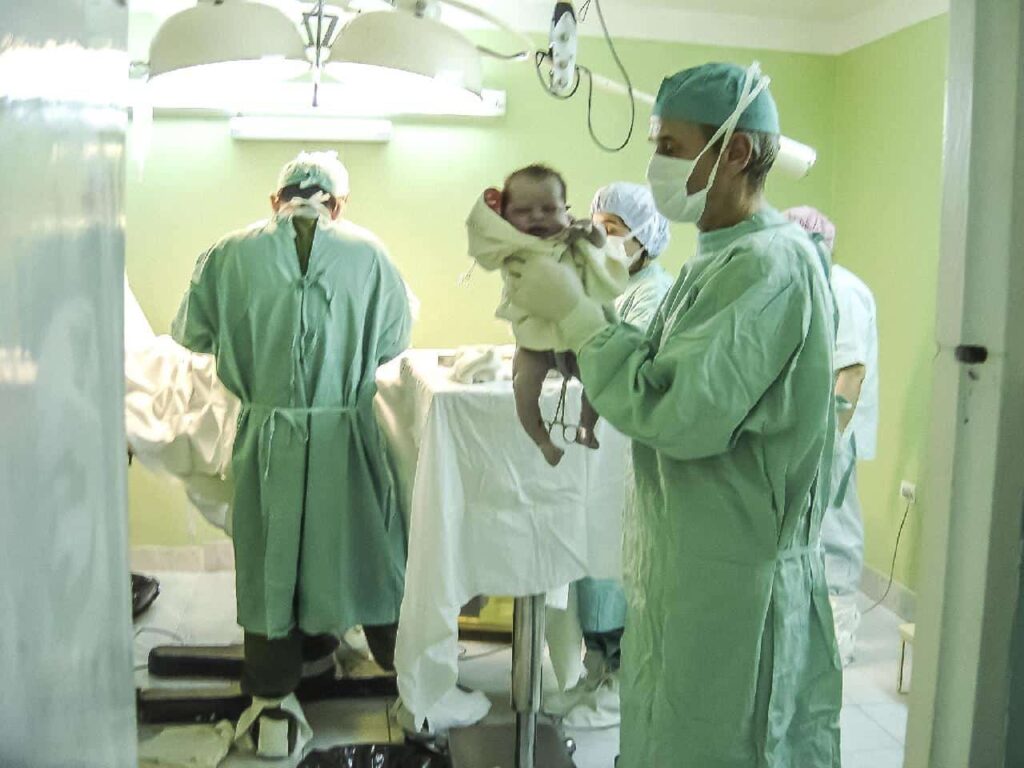
Perinatal nurses are those who care for women before, during, and after pregnancy. They help the mother and baby for the first few weeks of the newborn’s life. They educate patients and families about childbirth options, umbilical cord care, and more.
Moreover, they screen and assess patients for high-risk pregnancies and perform routine pregnancy tests. They can work alongside a physician or nurse-midwife during labor as well.
Postpartum Nurse
Postpartum nurse provides physical and emotional care to mothers and newborn babies during delivery. They work in hospitals and birth centers and often work with lactation consultants and labor and delivery nurses to ensure that a new mother recovers from the birth properly and is educated on how to care for an infant.
They also provide pain management and postpartum monitoring for the new mother.
Psychiatric Nurse
Psychiatric nurses care for the patients who suffer from mental health illnesses and those struggling with addiction and substance abuse issues. They assess and monitor patients, help administer medications, and work with an interdisciplinary team, including psychiatrists and social workers.
Psychiatric nurses work in hospitals, mental health facilities, medical offices, schools, correctional facilities, and community settings where mental healthcare is needed.
Radiology Nurse

Radiology nurses care for patients who need to undergo diagnostic imaging procedures (such as x-rays, MRIs, and CT scans) or for those undergoing radiation therapy for some illnesses, like cancer.
They educate the patients on the need for the procedure, prepare the patients on the day of the procedure, administer any contrast dyes, operate the machines, and monitor the patient after the procedure. They usually work in hospitals, diagnostic imaging facilities, or outpatient care facilities.
Transplant nurses
Transplant nurses care for the patients who need organ or tissue transplant surgeries and living donors who have volunteered to donate tissues or organs for transplant.
Their responsibility is to prepare patients for surgery, assist surgeons during harvest and donation procedures and provide patient education and crucial post-operative care, including monitoring for complications such as infection or organ rejection.
Trauma nurses
Trauma nurses are specialized in caring for patients with acute injuries or illnesses, including accidents, gunshot or stab wounds, assaults, and more. They work in emergency environments and are responsible for stabilizing patients. They also document the patient’s care and work with any law enforcement officers involved.
Wound Care Nurse

Wound care (WOC) nurses treat patients who have ostomies and serious wounds. This includes wound cleaning, debridement, and bandaging, amongst other things. They also help doctors assess whether further treatment, such as antibiotics or surgery, is necessary or not.
These nurses also help care for bedridden patients who have bedsores, people suffering from complications of diabetes, and may work in a hospital, nursing home, or other long-term care settings.
2. Non-hospital Based Jobs
A range of non-hospital nursing career opportunities is also available for RNs who do not want to work in the expeditious hospital environment. These jobs typically require at least a few years of clinical nursing experience. Here are some non-hospital based jobs for nurses:
Clinical Nurse Educator

Nurse educators are the registered nurses (RNs) who have earned advanced nursing degrees that allow them to teach the nursing curriculum at colleges and universities.
They serve as faculty members in both teaching hospitals and nursing schools, transferring their valuable knowledge, experience, and skills to their students, who are going to ultimately serve as the next generation of nurses.
Many nurse educators also work in clinical settings. The best nurse educators have excellent communication abilities, exhibit exceptional leadership qualities, and have in-depth, comprehensive knowledge in their given field.
Public Health Nurse
Public health nurses serve a community by promoting health and wellness and providing medical services. The major part of their job is working with underprivileged and underserved populations, providing them education and resources.
Public health nurses can also work in local government, such as county or city health departments or private public-health agencies.
Home Health Nurse

Home health nursing staff cares for patients in their homes, performing different tasks if patients or their families are unable to care for themselves. This is the specialty of RNs, LVNs/LPNs, and nurse assistants. Their tasks include medication administration, taking vitals, wound care, assisting with mobility, and more.
Travel Nurse
Travel nurses are from various clinical backgrounds who work for independent staffing agencies. They are assigned different care areas on a temporary basis to fill in short-term employment gaps. These nurses can work internationally or domestically, fulfilling the needs.
They perform the tasks of standard registered nurses but may need to adapt to certain challenges such as language differences or particular local illness/disease outbreaks.
Forensic Nurse

Forensic nurses are highly trained to care for victims of abuse and trauma. In addition to treating these patients, they also work alongside law enforcement to collect photograph injuries, evidence and even testify in court if necessary.
They are able to work in hospitals, usually in trauma or ER wards, or assist coroners and medical examiners.
Nurse Advocate
A nurse advocate works on behalf of patients to maintain the quality of care and protect patients’ rights. They are responsible for helping patients, and families navigate the healthcare system and act as an alliance between patients, healthcare providers, and insurance companies.
They also play a significant part in educating patients on healthcare decisions, resources, and insurance benefits and assist with any disputes a patient may have with their care.
Telephone Triage Nurse
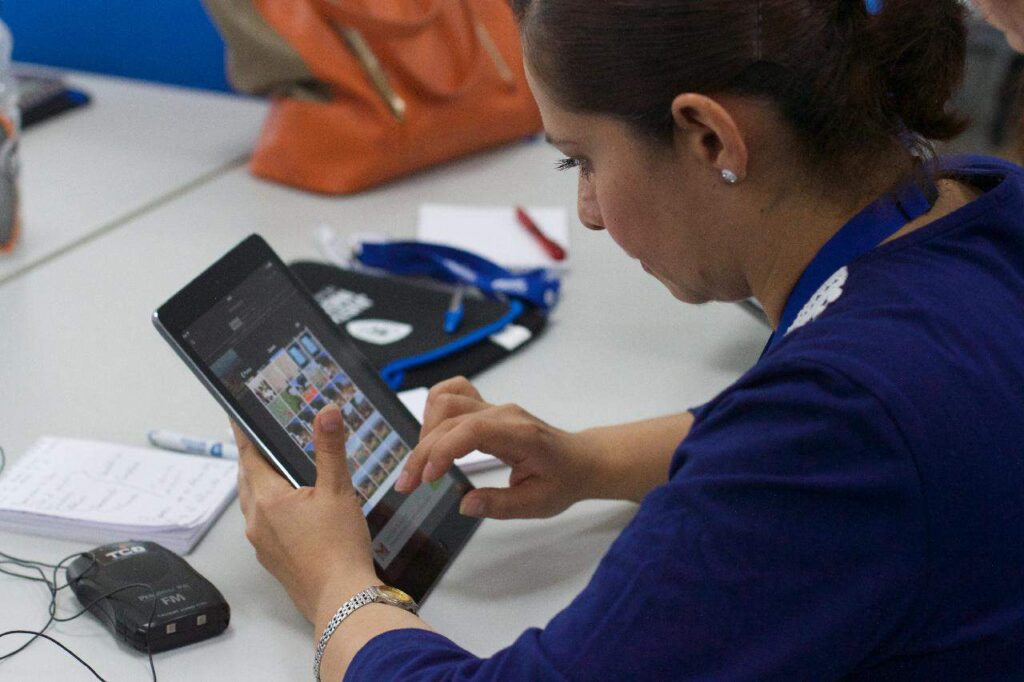

Telephone triage nurses are also known as telehealth nurses and TTNs. They provide care to patients over the phone or via video chats. They serve as crucial healthcare resources for those who live far away from a medical facility or need help and advice after-hours.
A telephone triage nurse helps to assess the patient’s medical issue and refer them to the proper line of care, whether that’s home care, a physician’s or specialist’s office, or the emergency room.
Nurse Writer
Nurse writers utilize their knowledge and skills to inform and educate others. They are able to communicate clinical and healthcare information through the writing process. The jobs rely on comprehensive training and expertise and require nurse writers to inform a broad audience.
Nurse writers can assist with medical documents, articles and blogs, manuscripts, brochures, and more.
Flight Nurse
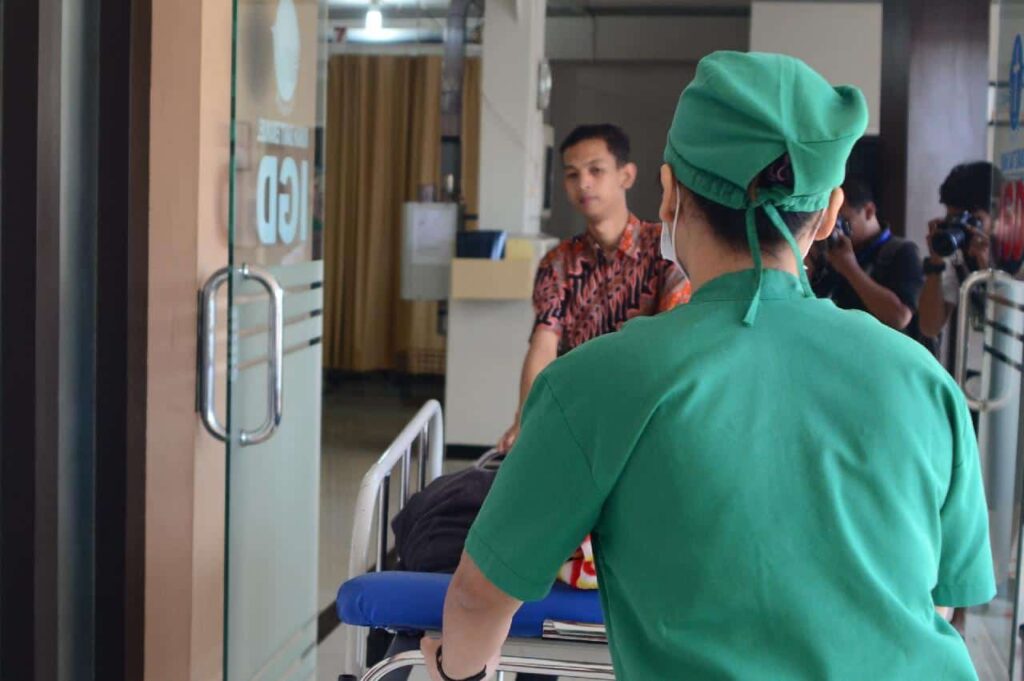

Flight nurses are also referred to as transport nurses. They provide critical care to patients en route to a hospital or medical facility onboard an aircraft, like a helicopter or a rescue flight.
They assess the patients, administer first aid, perform resuscitation and ventilation procedures, and monitor vital signs to keep the patients stable until arrival.
Moreover, they also assist in getting patients into and out of the aircraft, ensuring that they are secured safely once onboard. When they arrive at the hospital, flight nurses update the onsite medical staff to ensure a smooth hand-off.
Conclusion
The nursing field offers a range of career opportunities. Many of these paths allow nurses to go beyond bedside care and traditional workplace settings, such as hospitals and private practices.
The demand for nurses is constantly growing, and the nursing career path offers many worthwhile benefits like strong salaries, numerous opportunities, and a feeling of fulfillment.
Nursing is not meant for everyone. It asks for a very strong, intelligent, and compassionate person to take on the ills of the world with passion and purpose to maintain the health and well-being of the planet. No doubt we’re exhausted at the end of the day!
References:
NurseJournal.org: 50 Things You Can Do With a Nursing Degree
Gwynedd Mercy University: Types of Nursing Specialties: 20 Fast-Growing Nursing Fields
RegisteredNursing.org: Nursing Careers & Specialties for RNs
